Choosing the right motherboard is one of the most important decisions you’ll make when building a computer system. The motherboard, also known as the “backbone” of your PC, is crucial in determining compatibility, performance, and future expansion possibilities. It serves as a central hub, connecting all of your system’s essential components, from the processor to memory, storage devices, and expansion cards.
Choosing the best motherboard necessitates careful consideration and comprehension of numerous factors. We will delve into the key reviews, essential features, and important steps in this comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision. This guide will provide you with valuable insights and practical advice for selecting the best motherboard for your needs, whether you’re a seasoned PC builder or a first-time enthusiast.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a firm grasp on the critical factors to consider when selecting a motherboard, ensuring compatibility with your desired components, unlocking optimal performance, and allowing for seamless future upgrades. So let’s get started and explore the world of motherboards, so you can make an informed decision for your next computer build.
Socket Type and CPU Compatibility
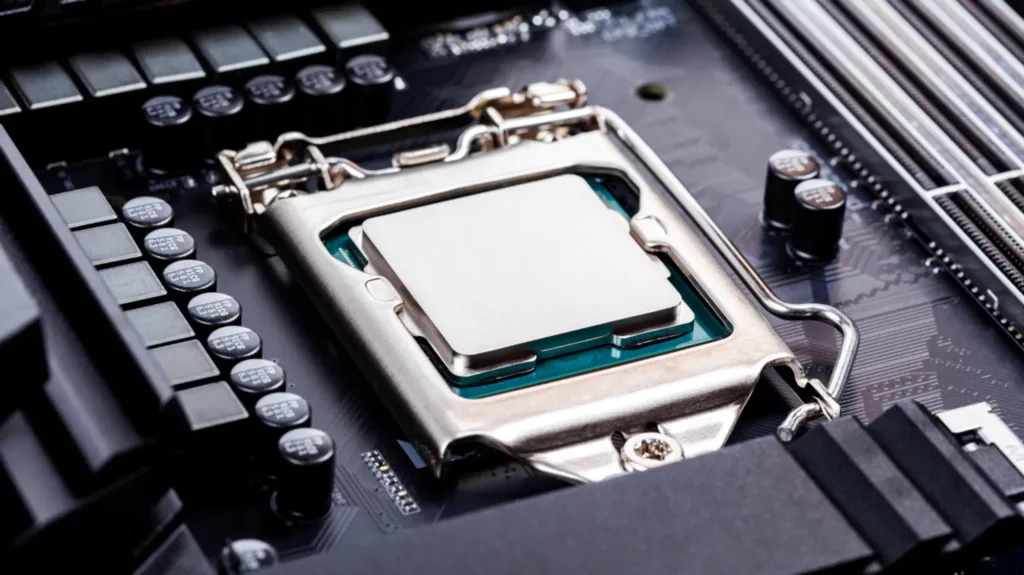

When it comes to building a computer system, matching the motherboard’s socket type with the chosen CPU is critical. The socket type refers to the physical structure and layout of the CPU socket on the motherboard, which determines the motherboard and CPU compatibility. Here’s why it’s critical to get a match:
- Proper Fit and Connection: The motherboard CPU socket is designed to accommodate a specific socket type. Each CPU has a particular number of pins arranged in a specific pattern that must perfectly align with the corresponding motherboard socket. The proper fit and connection between the CPU and motherboard are ensured by matching the socket type, allowing for stable and reliable performance.
- Electrical Compatibility: The socket type determines the CPU’s and motherboard’s electrical compatibility. Different CPU models and generations necessitate unique power delivery and voltage regulation mechanisms, which are designed and implemented within the motherboard’s socket. A mismatched socket type can cause improper power delivery, voltage inconsistencies, and potential CPU or motherboard damage.
- Feature Support: The socket type also determines the CPU’s feature support. Different CPU models have different features, such as overclocking, integrated graphics, and memory support. To fully utilise the CPU’s capabilities, the motherboard’s socket must support these features. A mismatched socket type may limit or disable certain features, preventing you from fully utilising the CPU’s capabilities.
- Performance optimisation is achieved by matching the motherboard’s socket type with the CPU of choice. The CPU and motherboard work together to provide the best performance possible, taking advantage of the CPU’s architecture, clock speeds, and core counts. A compatible socket type ensures efficient communication between the CPU and other system components, maximising overall system performance.
- Future Upgradability: Choosing a motherboard with a compatible socket type allows for CPU upgrades in the future. As technology advances, new CPU models with various socket types are released. By selecting a motherboard that supports the current socket type and is compatible with higher-end CPUs, you can upgrade in the future without having to replace the entire motherboard.
In conclusion, matching the motherboard’s socket type with the CPU of choice is critical for proper fit, electrical compatibility, feature support, performance optimisation, and future upgradability. A compatible socket type is essential for a stable and high-performing computer system. To ensure a seamless match between the CPU and motherboard socket type, always check the specifications and compatibility lists provided by the motherboard manufacturer and CPU vendor.
There are numerous types of CPU sockets available on the market, but the most common are:
- LGA 1151 – This is the most common Intel processor socket. It was first released in 2015 and is compatible with Intel Core processors from the sixth, seventh, eighth, and ninth generations.
- LGA 1200 – Intel’s most recent socket, compatible with 10th and 11th-generation Intel Core processors.
- AM4 – This is the most common AMD processor socket. It debuted in 2016 and is compatible with Ryzen 1000, 2000, 3000, and 5000 processors.
- AM5 – AMD’s most recent socket, compatible with Ryzen 6000 series processors.
Form Factor Selection
Different Form Factors of Motherboard:
- ATX – The ATX form factor is the most widely used for motherboards. It measures 12 inches wide by 9.6 inches long. ATX motherboards are packed with features and expansion slots, making them an excellent choice for high-end gaming PCs and workstations.
- The MicroATX form factor is a scaled-down version of the ATX form factor. It measures 9.6 inches wide by 9.6 inches long. MicroATX motherboards are an excellent choice for low-cost users and small form factor builds.
- Mini-ITX – The smallest form factor for motherboards is Mini-ITX. It measures 6.7 inches wide by 6.7 inches long. Mini-ITX motherboards are ideal for building HTPCs and other small form-factor computers.
There are a few less common form factors, such as Extended ATX (E-ATX) and Nano-ITX. E-ATX boards are larger than ATX boards, and Nano-ITX boards are more minor than Mini-ITX boards.
The size of the case that you can use is determined by the form factor of the motherboard. For example, an ATX motherboard cannot be used in a case designed for a MicroATX motherboard.
It is critical to consider the form factor of your case when selecting a motherboard. The form factor of your case can be found in the specifications of your case or on the manufacturer’s website.
Expansion Slots in Motherboard
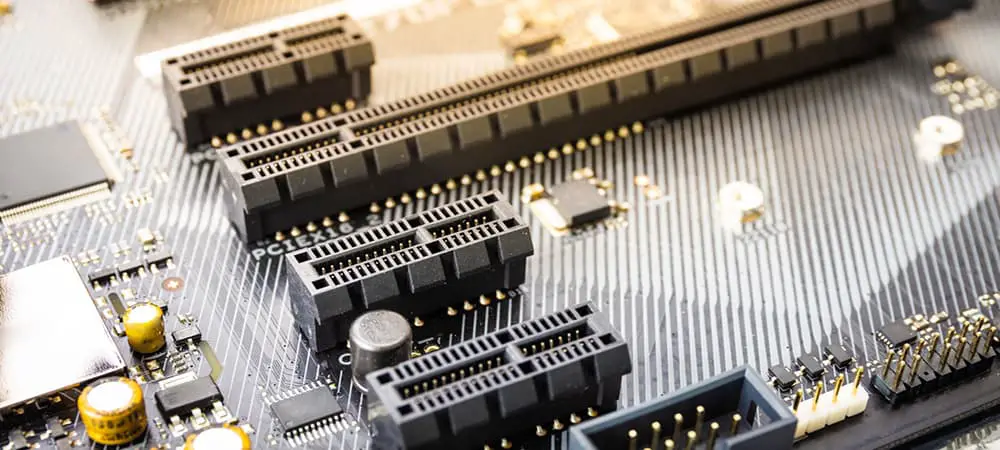
- PCI Express (PCIe) Slots: High-speed expansion cards such as graphics cards, sound cards, network adapters, and storage controllers are commonly used in PCIe slots. They are available in a variety of sizes, including x16 (for graphics cards), x8, x4, and x1 (for other expansion cards). PCIe slots provide faster data transfer rates and better performance than older slots such as PCI and AGP.
- PCI Slots: PCI slots were widely used in older motherboards but have been largely replaced by PCIe slots. Some motherboards, however, still include PCI slots for compatibility with older expansion cards that may not be PCIe compliant. PCI slots are typically used for low-bandwidth devices such as sound cards, modems, legacy devices, and expansion cards.
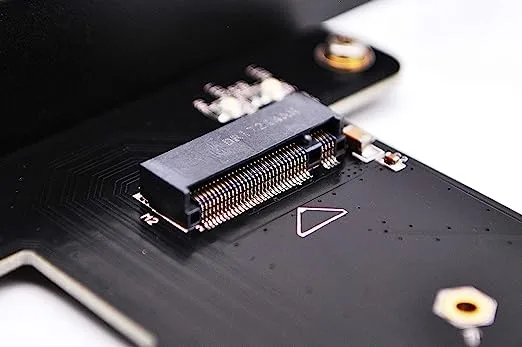
- M.2 Slots: M.2 slots are becoming increasingly popular for high-speed storage devices such as SSDs. M.2 slots support the NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) protocol, which allows for faster data transfers than traditional SATA connections. M.2 slots are available in a variety of lengths and keying types (B, M, or B+M) to accommodate various M.2 SSD sizes and interfaces.
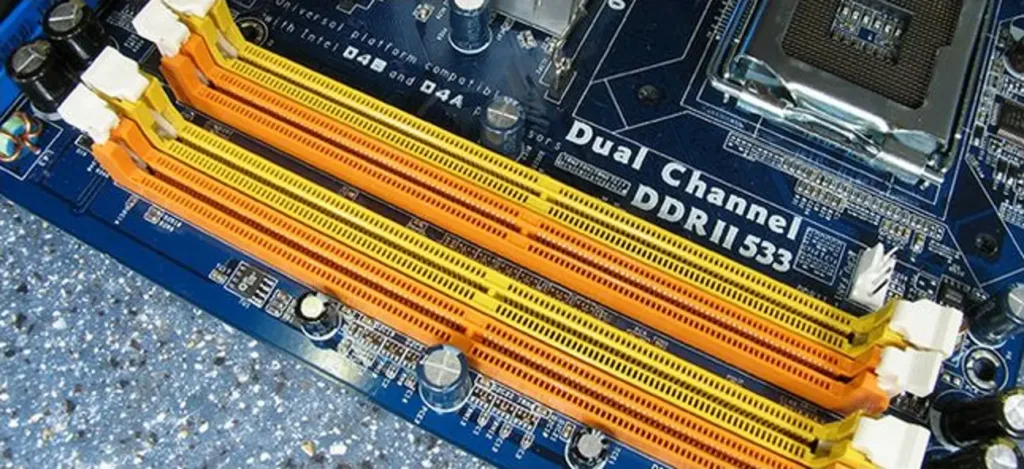

- RAM Slots: RAM slots are used on motherboards to install memory modules (RAM). The number of RAM slots varies depending on the form factor and chipset of the motherboard. DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) slots for desktop systems and SODIMM (Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module) slots for laptops and small form factor systems are the most common RAM slot types.
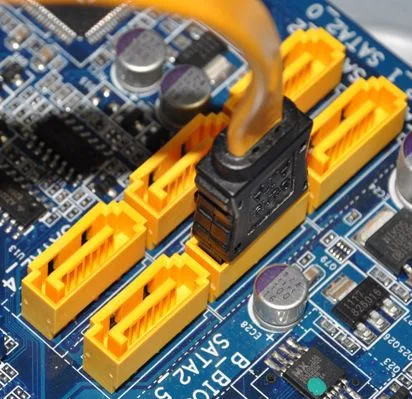
- SATA Ports: SATA ports on the motherboard, while not technically expansion slots, allow you to connect SATA devices such as hard disc drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical drives. SATA ports enable high-speed data transfer between the motherboard and storage devices.
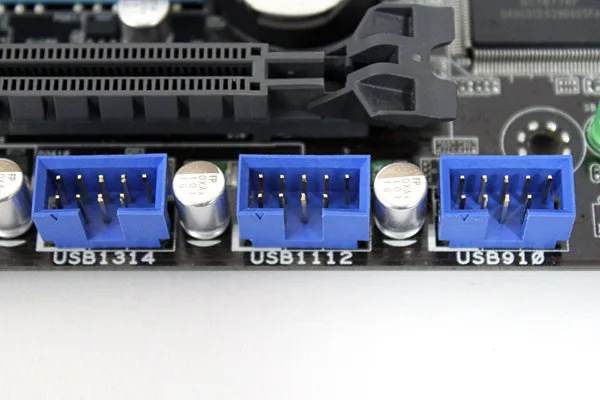

- USB Headers: USB headers are motherboard connectors that allow you to add additional USB ports to the system. These headers are typically used to connect USB ports on the front panel of a computer case, allowing USB devices easy access.
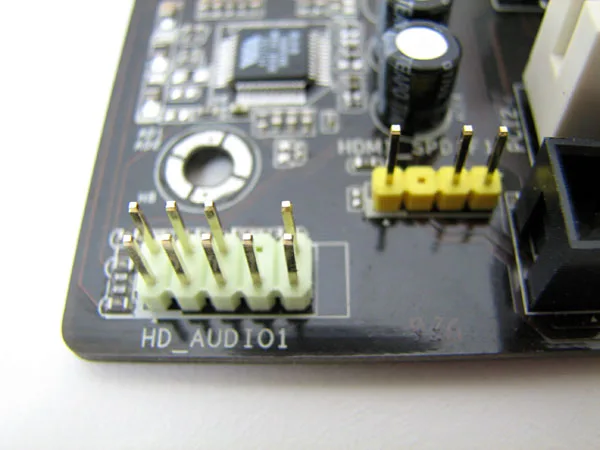

- Audio Headers: Audio headers on the motherboard connect to front panel audio jacks on the computer case, allowing audio input and output.
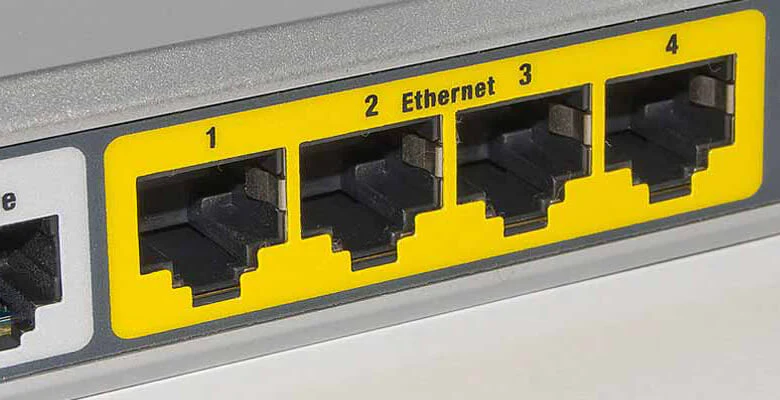

- Ethernet Port: The Ethernet port on the motherboard provides your computer with a wired network connection. It gives you the ability to connect to a local network or the internet.
When choosing a motherboard, it is critical to consider the number and type of expansion slots required for specific components. It is critical to evaluate the number and type of expansion slots required for specific components to ensure component compatibility, future expandability, performance optimisation, functionality, customization, and budget optimisation. It enables you to choose a motherboard that meets your current requirements while also allowing for future upgrades and enhancements. When selecting a motherboard, consider your component requirements as well as the available expansion slots to build a well-balanced and future-proof system.
RAM Compatibility
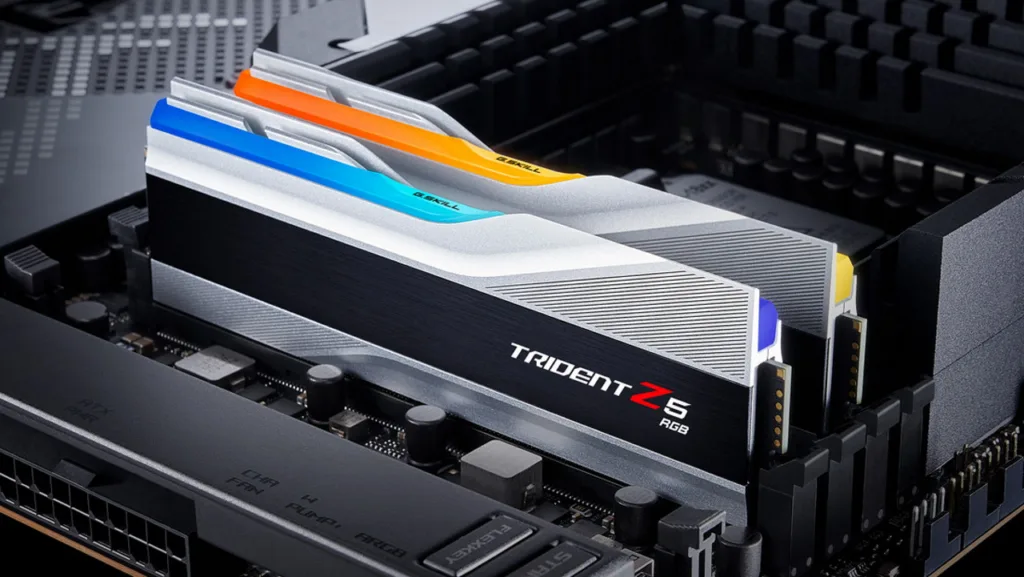

When building a computer system, it is critical to check the memory compatibility of the motherboard.
Checking the memory compatibility of the motherboard is critical for system stability, performance optimisation, capacity considerations, dual-channel or quad-channel support, XMP support, and compatibility with other components. It ensures that the memory modules you select will work in tandem with your motherboard, resulting in a stable and high-performing computer system. To select memory modules that are officially supported and guaranteed to work with your specific motherboard, always refer to the motherboard’s specifications and compatibility lists provided by the manufacturer.
When determining the memory compatibility of a motherboard, several factors must be considered. These are some examples:
- Memory type: Motherboards can only support a limited number of memory types. DDR3 and DDR4 memory are the most common types of memory.
- Memory speed: Motherboards can only support certain memory speeds. Memory speed is measured in megahertz (MHz).
- Memory voltage: Motherboards can only support certain memory voltages. Memory voltage is measured in volts.
- Memory capacity: Motherboards can only support so much memory. The memory capacity of a motherboard is measured in gigabytes (GB).
- Memory slots: Each motherboard has a fixed number of memory slots. How much memory you can install is determined by the number of memory slots on a motherboard.
- Memory compatibility list: Memory compatibility lists (or HCLs) are frequently published by motherboard manufacturers. The HCL lists the memory types that have been tested and proven to work with the motherboard.
Check the motherboard specifications to see what type, speed, voltage, capacity, and number of memory slots are supported. You should also check the HCL of the motherboard to ensure that the memory you want to buy is compatible with it.
Storage Options while choosing a motherboard

It is critical to consider your storage requirements when selecting a motherboard. Because the motherboard determines the type and number of storage devices that can be used, it must have the features that you require.
Here are some things to think about when selecting a storage motherboard:
- Storage Capacity: Each motherboard supports a different number of storage devices such as hard disc drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). You can ensure that the motherboard has enough SATA ports or M.2 slots to accommodate the desired number of drives by considering storage requirements. This is especially important if you require a lot of storage space, such as for large media files, games, or data-intensive applications.
- Storage Interface: For M.2 SSDs, motherboards support various storage interfaces such as SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express). It is critical to check the storage interfaces supported by the motherboard and ensure that they are compatible with your storage devices. To take full advantage of an NVMe SSD’s high-speed capabilities, for example, you’ll need a motherboard with an M.2 slot that supports NVMe.
- RAID Support: RAID configurations (Redundant Array of Independent Discs) are used to improve data storage performance, reliability, or both. If you intend to use RAID arrays, you must select a motherboard that supports the desired RAID level (e.g., RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5) and includes the required RAID controller or chipset. This ensures that your RAID setup has proper hardware-level support.
- Storage Expansion: Taking storage requirements into account allows for future expansion. As your data needs grow, you may want to add more storage devices. You can easily expand your storage capacity by selecting a motherboard with additional storage connectivity options, such as extra SATA ports or M.2 slots, without the need for additional hardware upgrades or replacements.
- Storage Speed and Performance: The speed and performance of storage devices vary. Some motherboards include features or technologies that improve storage performance, such as PCIe Gen 4 support for faster NVMe SSDs. By considering storage requirements, you can select a motherboard with the features needed to fully utilise the potential of your storage devices, resulting in faster data access speeds and overall system performance.
- Storage Controller Compatibility: If you intend to use additional storage controllers, such as RAID controllers or PCIe-based storage expansion cards, you must ensure that the motherboard has the necessary expansion slots and compatibility. This allows for the storage controllers to be seamlessly integrated into the system, ensuring proper operation and data transfer rates.
I/O Ports and Connectivity

It is critical to inspect the rear I/O panel of a motherboard for necessary ports such as USB, Ethernet, audio, and video outputs. Here’s why it’s critical to think about the available ports:
- Connectivity: The primary means of connecting external devices to your computer system is through the rear I/O panel. Examining the available ports ensures that you have the connectivity options you need to connect peripherals and devices like USB drives, keyboards, mice, monitors, speakers, and networking cables. In the absence of the required ports, you may require additional adapters or expansion cards, which can be inconvenient and complicate your setup.
- USB Ports: USB ports are essential for connecting a variety of devices, such as external hard drives, printers, cameras, and smartphones. Examining the number and type of USB ports on the rear I/O panel ensures that you have enough ports for your devices. For optimal data transfer speeds, consider the USB version (e.g., USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1) and its compatibility with your devices.
- Ethernet Port: The rear I/O panel’s Ethernet port allows you to connect your computer to a wired network for high-speed internet access and local network connectivity. Examining the availability of an Ethernet port ensures that you can create a dependable and fast network connection, which is especially important for tasks like online gaming, streaming, or data-intensive work.
- Audio Ports: The audio ports on the back I/O panel allow you to connect speakers, headphones, or microphones to your computer directly. Examining the availability of audio jacks ensures that you can connect your audio devices without the use of additional adapters or cables. It’s critical to look for standard audio jacks such as Line-In, Line-Out, and Mic-In, as well as any specialised audio ports for enhanced audio configurations.
- Video Outputs: You can connect monitors or displays to your computer system using the video outputs on the rear I/O panel. Examining the video outputs available, such as HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, or VGA, ensures compatibility with your display devices. To ensure optimal display quality, consider the maximum supported resolution and refresh rate of the video outputs.
- Other Ports: The rear I/O panel may also include PS/2 ports for legacy devices, S/PDIF ports for digital audio connections, and specialised ports for specific functionalities such as Thunderbolt or eSATA. Examining the availability of these ports enables you to connect devices or use specific features based on your needs.
Importance of Power Delivery and Overclocking in Motherboard
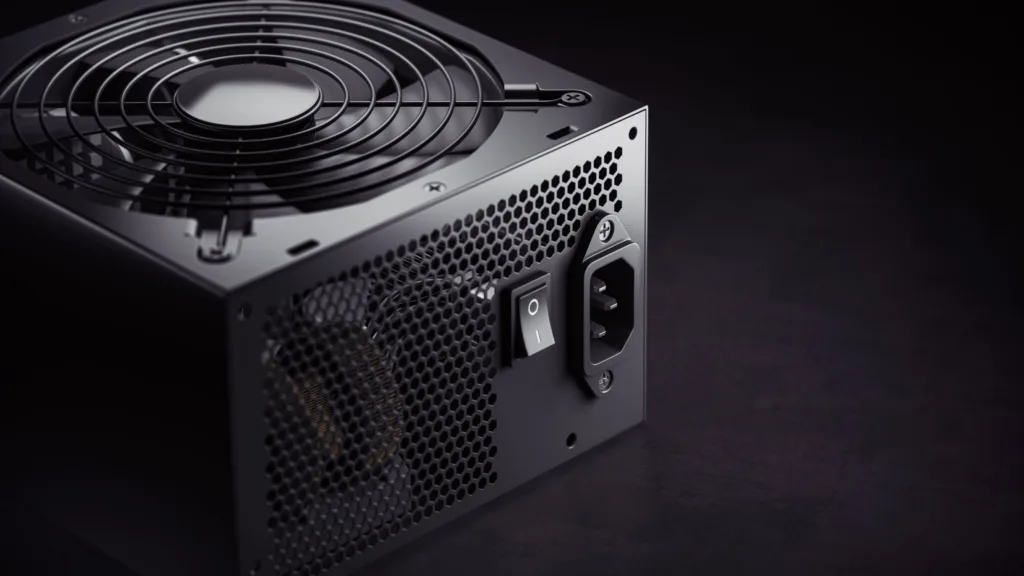

A reliable power delivery system (PDSS) is required for overclocking or power-hungry motherboard components. A PDSS is in charge of delivering power to the CPU, GPU, and other motherboard components. If the PDSS is not sufficiently robust, it can cause component instability or even damage.
Here are some of the advantages of having a strong PDSS:
- Overclocking: Overclocking is the process of increasing a component’s clock speed beyond its factory settings. This can improve performance, but it also increases the component’s power demand. A strong PDSS can help to ensure that the component has enough power to keep running at its overclocked speed without overheating or becoming unstable.
- Components that consume a lot of power: Some components, such as high-end graphics cards, can consume a significant amount of power. A strong PDSS can assist in ensuring that these components have enough power to perform optimally without overheating or becoming unstable.
- Stability: A strong PDSS can help to improve system stability. This is critical when overclocking and using power-hungry components. A stable system is less likely to fail or crash.
Here are some things to look for when selecting a motherboard with a strong PDSS:
- Power phases: The number of power phases indicates the amount of power that the PDSS can deliver. More power phases generally imply that the PDSS can deliver more power, which is advantageous for overclocking and the use of power-hungry components.
- VRM heatsinks: VRM heatsinks aid in the cooling of PDSS components. This is critical for avoiding overheating, which can lead to instability or damage.
- Power delivery design: The PDSS’s design can have an impact on its performance. Some designs are more efficient than others, resulting in improved performance and lower heat output.
You can help to ensure that your system is stable and performs well by selecting a motherboard with a strong PDSS.
Importance of VRM quality and adequate cooling solutions in the motherboard
The VRM, or Voltage Regulator Module, is in charge of converting the power supply’s 12V power into the lower voltages required by the CPU and other components. A good VRM is critical for ensuring your system’s stability and performance.
When evaluating a motherboard’s VRM quality, there are a few things to look for:
- The number of power phases: The number of power phases indicates the amount of power that the VRM can deliver. More power phases generally imply that the VRM can deliver more power, which is advantageous for overclocking and the use of power-hungry components.
- The quality of the VRM components: The quality of the VRM components is important in determining the overall quality of the VRM. High-quality VRM components can withstand higher temperatures and deliver more power without overheating or becoming unstable.
- VRM heatsinks: VRM heatsinks aid in the cooling of VRM components. This is critical for avoiding overheating, which can lead to instability or damage.
- The power delivery design: The design of the power delivery system can also affect its performance. Some designs are more efficient than others, which can lead to better performance and less heat output.
Adequate cooling solutions are also important for ensuring that the VRM stays cool and doesn’t overheat. VRM heatsinks are a good way to help keep the VRM cool, but they may not be enough for high-end systems or overclocking. In these cases, additional cooling solutions, such as water cooling, may be necessary.
Additional onboard features
- Integrated Wi-Fi: With integrated Wi-Fi, you can connect to a wireless network without installing a separate Wi-Fi card. This can be useful if you don’t have a wired connection or if you want to move your computer around easily.
- Bluetooth connects you to Bluetooth devices such as wireless mice, keyboards, headphones, and speakers. This is useful for a variety of tasks, including gaming, listening to music, and watching videos.
- Audio codecs: Audio codecs are in charge of your computer’s sound quality. High-quality audio codecs on motherboards can produce better sound than low-quality audio codecs on motherboards. This is important for gamers, audiophiles, and anyone else who appreciates high-quality sound.
- Other onboard features include: Other onboard features that can improve convenience and functionality are as follows:
- USB ports: USB ports allow you to connect peripherals such as printers, scanners, external hard drives, and other devices.
- An Ethernet port enables you to connect your computer to a wired network.
- M.2 slots are a newer type of storage slot that can accommodate SSDs. SSDs are faster than hard drives, so M.2 slots can help your computer perform better.
- PCIe slots: High-performance expansion cards, such as graphics cards and sound cards, use PCIe slots.
Importance of researching the manufacturer’s reputation and customer support while choosing a motherboard
When selecting a motherboard, it is critical to investigate the manufacturer’s reputation and customer support. This is because the motherboard is a critical component of your computer, and you want to ensure that you are purchasing a product from a reputable company with excellent customer service.
Here are some of the reasons why it is critical to investigate the manufacturer’s reputation and customer service:
- Reliability: A reliable motherboard is more likely to be produced by a reputable manufacturer. This means your motherboard will be less likely to fail, saving you time and money in the long run.
- Updates: A reputable manufacturer is more likely to provide motherboard updates. This can improve your motherboard’s performance and fix any bugs that may be present.
- Customer service: If you have any problems with your motherboard, good customer service can be invaluable. A reputable manufacturer will have a team of experts who can assist you in troubleshooting and resolving any issues that may arise.
Here are some things you can do to learn more about the manufacturer’s reputation and customer service:
- Examine online reviews: Online reviews can be a great way to learn about the manufacturer’s reputation and customer service from other users.
- Visit the following website: The website of the manufacturer should include information about its warranty and customer support policies.
- Interact with other users: Inquire with anyone you know who has used a motherboard from the manufacturer about their experience.
Here are some of the most reputable motherboard manufacturers:

- Asus: Asus is a Taiwanese company that has been manufacturing motherboards since 1989. Asus is known for its high-quality products and excellent customer support.

- Gigabyte: Gigabyte is a Taiwanese company that has been manufacturing motherboards since 1995. Gigabyte is known for its innovative products and competitive prices.

- MSI: MSI is a Taiwanese company that has been manufacturing motherboards since 1986. MSI is known for its high-performance products and stylish designs.
Significance of setting a budget and balancing features and quality within budget constraints.
When selecting a motherboard, it is critical to set a budget and balance features and quality within that budget. This is because motherboard prices can vary greatly, and you want to ensure that you are getting the best motherboard for your money.
Some of the reasons why it is critical to set a budget and balance features and quality within budget constraints are as follows:
- Motherboard prices range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Setting a budget is essential to avoid overspending.
- Motherboards have a variety of features, including support for various processors, memory types, storage devices, and expansion cards. When selecting a motherboard, it is critical to consider the features that you require or desire.
- Quality: Different manufacturers produce motherboards of varying quality. It is critical to select a motherboard from a reputable manufacturer with a high-quality reputation.
Here are some of the things you can do to set a budget and balance features and quality within budget constraints:
- Set a budget: Decide how much you are willing to spend on a motherboard.
- Consider your needs: Think about what features you need or want in a motherboard.
- Do your research: Read reviews and compare prices to find the best motherboard for your needs and budget.
Compatibility between the motherboard and chosen components
Before assembling a computer, make sure that the motherboard and the components you’ve chosen are compatible. This is because different components may not be compatible with one another, which can cause issues such as system instability, crashes, or even component damage.
Here are some steps you can take to ensure compatibility between the motherboard and the selected components:
- Examine the specifications of the motherboard. The specifications of the motherboard will list the types of components that are compatible with the motherboard.
- Examine the specifications of the components. The specifications of the components will list the types of motherboards that are compatible with the components.
- Make use of a compatibility checker. There are numerous websites and software programmes available to assist you in determining compatibility between the motherboard and the selected components.
Conclusion
Finally, while establishing or upgrading a computer system, selecting the appropriate motherboard is crucial. It is the foundation for all other components, assuring compatibility and providing necessary features and functionality.
Further Read:
Best Motherboard under 10000 Rs. for AMD and Intel Processors
Best GPU under 30000 Rs. in 2023
Best Processor/ CPU Under 15000 For Gaming

Ajay Kumar is an experienced author and the founder of Techneg.co.in, a platform dedicated to providing insightful content on technology


![Affordable Laptops Under 50,000 – Which One’s Best for Work from Home? [2025 Edition]](https://techneg.co.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Affordable-Laptops-Under-50000-768x432.png)



![Best CPU Processor Under 20,000 in India [2025 Edition]](https://techneg.co.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Best-CPU-Processor-Under-20000-in-India-2025-Edition-768x432.png)